Install GitLab Using Docker Compose
This article is for those looking for a detailed and straightforward guide on installing GitLab using Docker Compose.
GitLab is an open-source end-to-end software development platform with built-in version control, issue tracking, code review, CI/CD, and more.
💾 You can find the repository used in this guide on GitHub.
We’ll use Traefik as our reverse proxy. It’ll handle obtaining cryptographic certificates from Let’s Encrypt for your domain names and route requests to the corresponding services based on those domains.
❗ To obtain cryptographic certificates, you will need A-type records in the external DNS zone, which point to the IP address of your server where Traefik is installed. If you have created these records recently, you should wait before starting the installation of the services. Full replication of these records between DNS servers can take from a few minutes to 48 hours or even longer in rare cases.
In this guide, we will consider the case where you already have a server with Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS installed on it.
You can find detailed information on how to install Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS in my guide “Install Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS”.
Docker Engine and Docker Compose must also be installed on the server.
You can learn how to install Docker Engine on Ubuntu Server by reading Install Docker Engine and Docker Compose on Ubuntu Server”.
In addition, OpenSSH must be installed on the server, and port 22 must be open in order to be able to connect to the server using the SSH protocol.
To install OpenSSH on the server you can use the command:
sudo apt install openssh-serverIf you plan to connect to the server using the Windows operating system, you can use PuTTY or MobaXterm.
This guide covers connecting to the server using the terminal emulator iTerm2, installed on the macOS operating system.
💡 Please note, you will need to open the following TCP ports for access to the services:
- TCP port 80 - to obtain a free cryptographic certificate through the Let’s Encrypt certification center.
- TCP port 443 - to access the GitLab web interface.
- TCP port 2222 - for secure SSH Git operations, user SSH key management, encrypted data transfer, and server administration tasks.
We connect to the server on which GitLab is planned to be installed.
Now it is necessary to create networks for your services.
We create a network for Traefik using the command:
docker network create traefik-network
We create a network for GitLab using the command:
docker network create gitlab-network
Next, you need to clone the repository that contains the configuration files, which include all the necessary conditions for GitLab to work.
You can clone the repository using the command:
git clone https://github.com/heyvaldemar/gitlab-traefik-letsencrypt-docker-compose.git
Navigate to the directory with the repository using the command:
cd gitlab-traefik-letsencrypt-docker-compose
Next, you need to change the variables in the .env file according to your requirements.
💡 Note that the .env file should be in the same directory as gitlab-traefik-letsencrypt-docker-compose.yml.
Now let’s start GitLab with the command:
docker compose -f gitlab-traefik-letsencrypt-docker-compose.yml -p gitlab up -d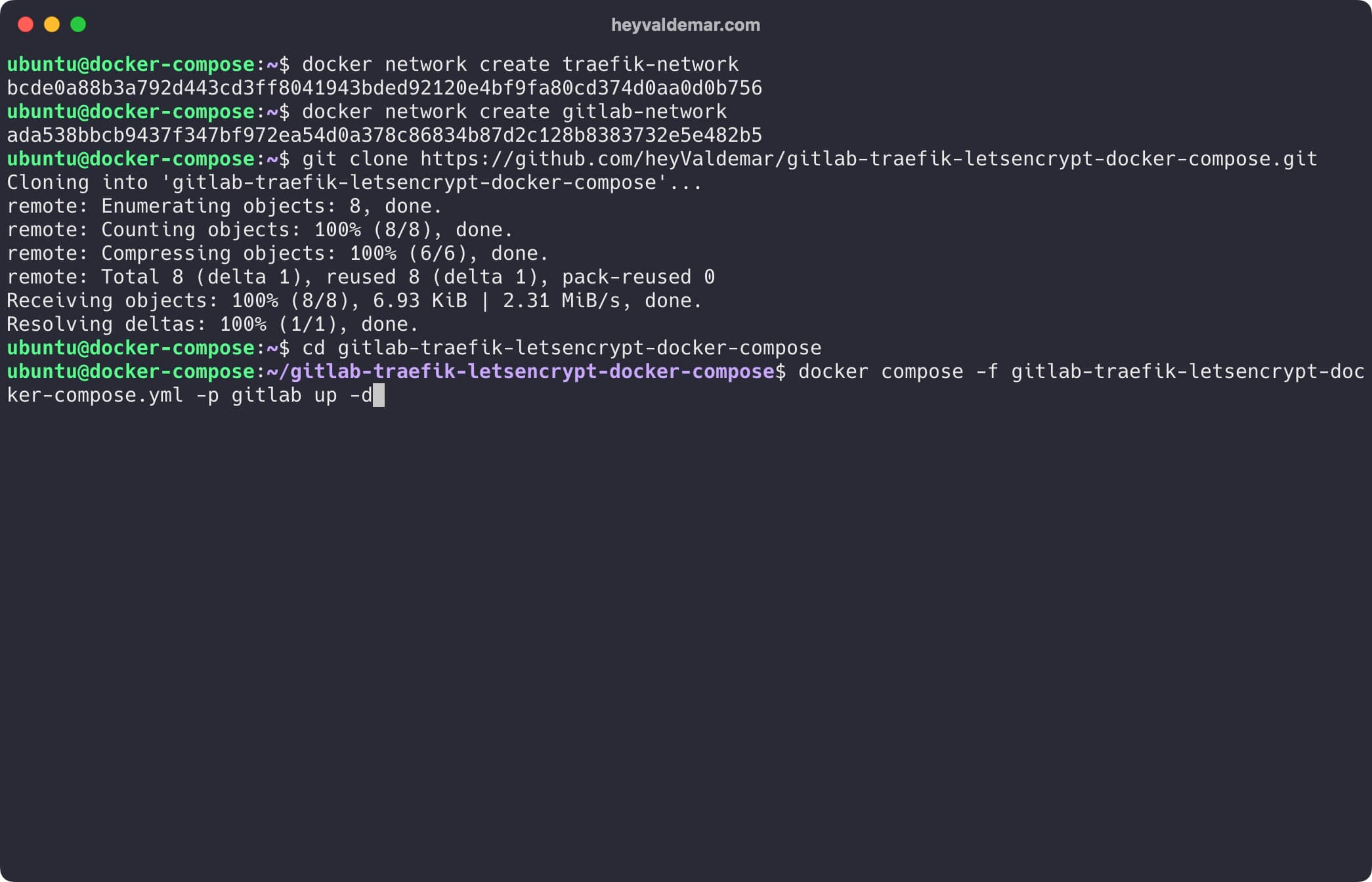
Now, let’s retrieve the password for the root user. This will allow you to log into the GitLab management panel.
Use the following command:
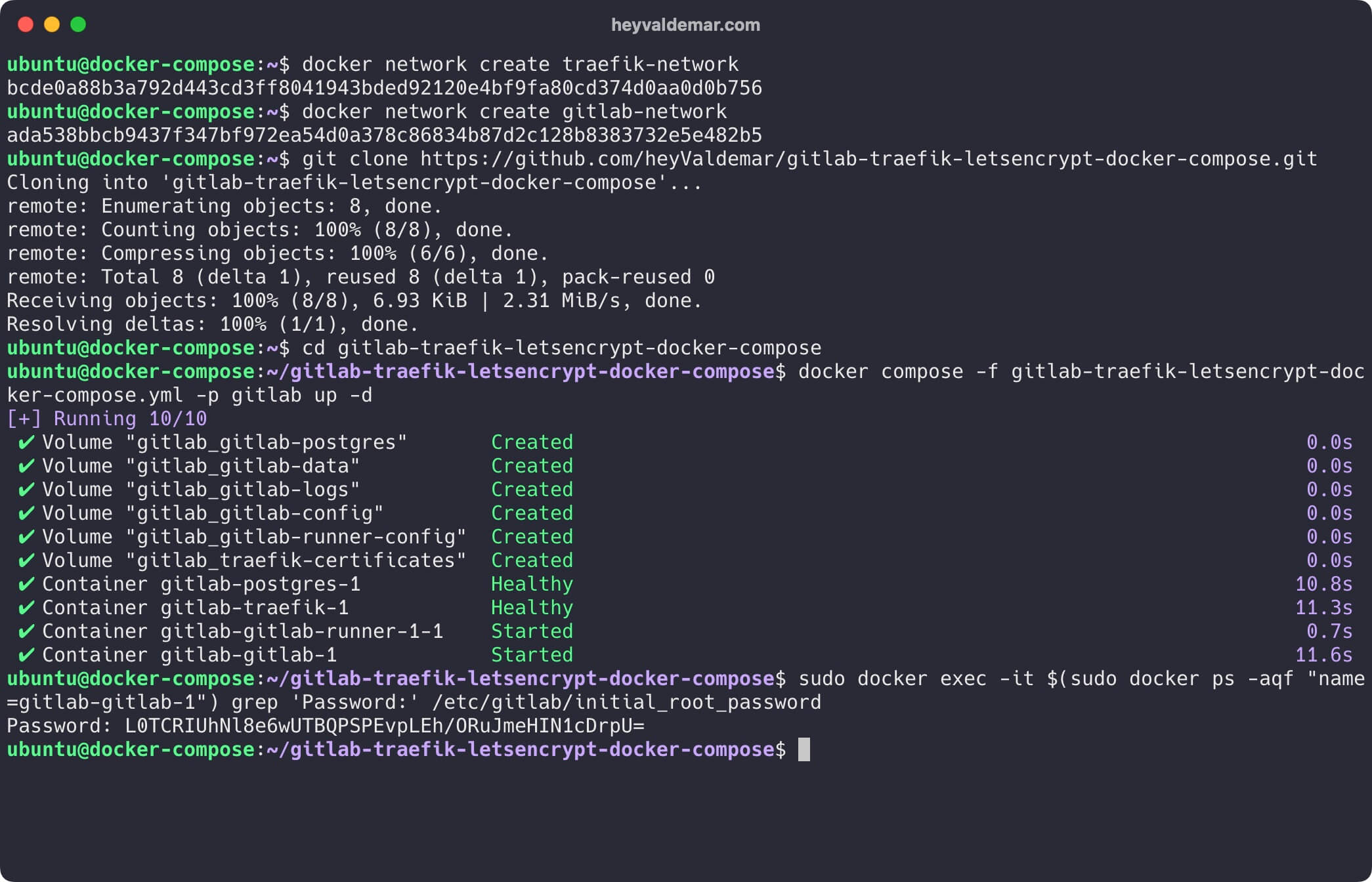
sudo docker exec -it $(sudo docker ps -aqf "name=gitlab-gitlab-1") grep 'Password:' /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password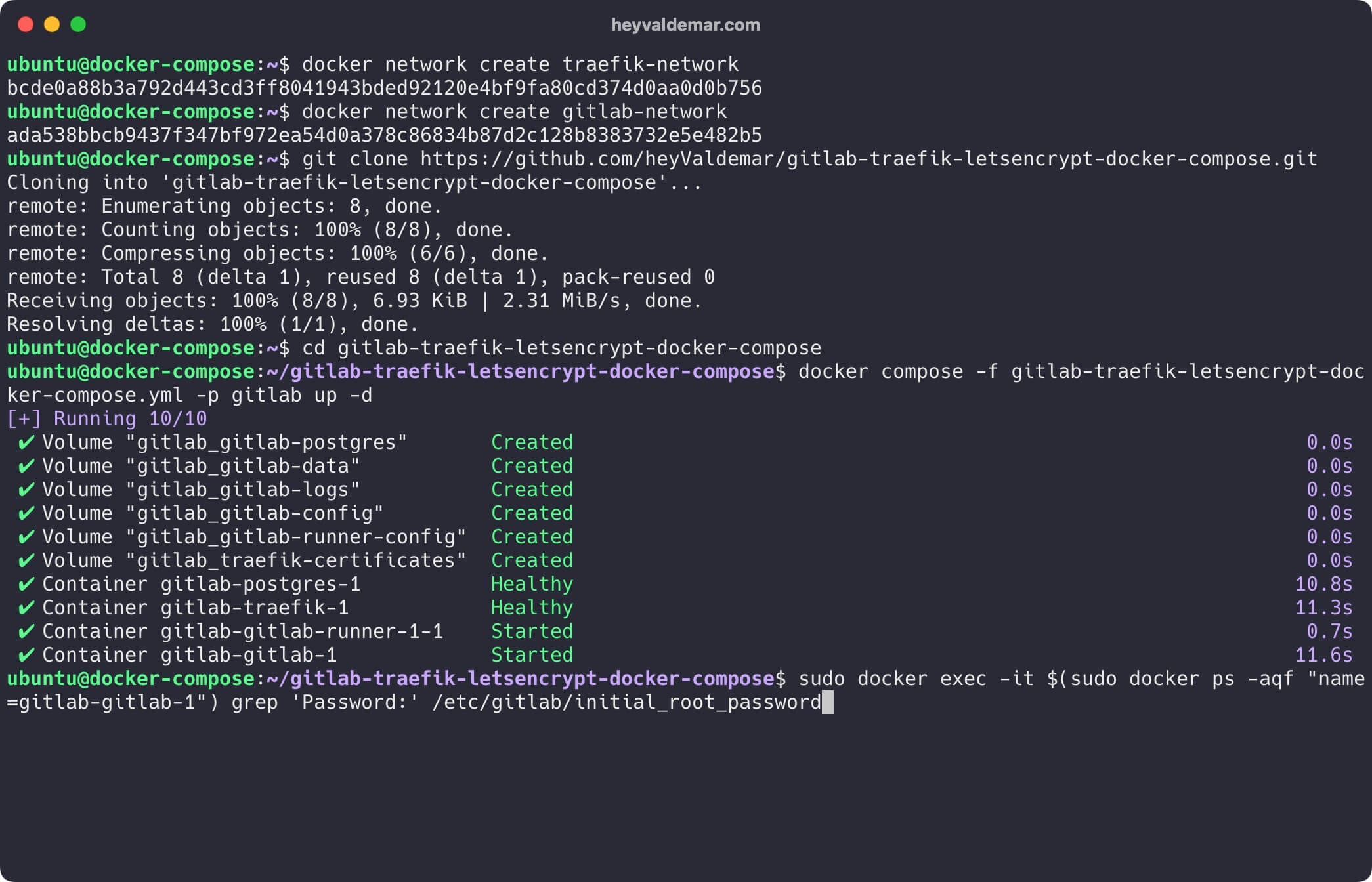
The password for the root user has been successfully retrieved.
To access the GitLab management panel, go to https://gitlab.heyvaldemar.net from your workstation, where gitlab.heyvaldemar.net is the domain name of my service. Accordingly, you need to specify your domain name that points to the IP address of your server with the installed Traefik service, which will redirect the request to GitLab.
💡 Note that you need to specify the domain name of the service, previously defined in the .env file.
Use root as the username and the previously obtained password, then click the “Sign in” button.
Welcome to the GitLab control panel.
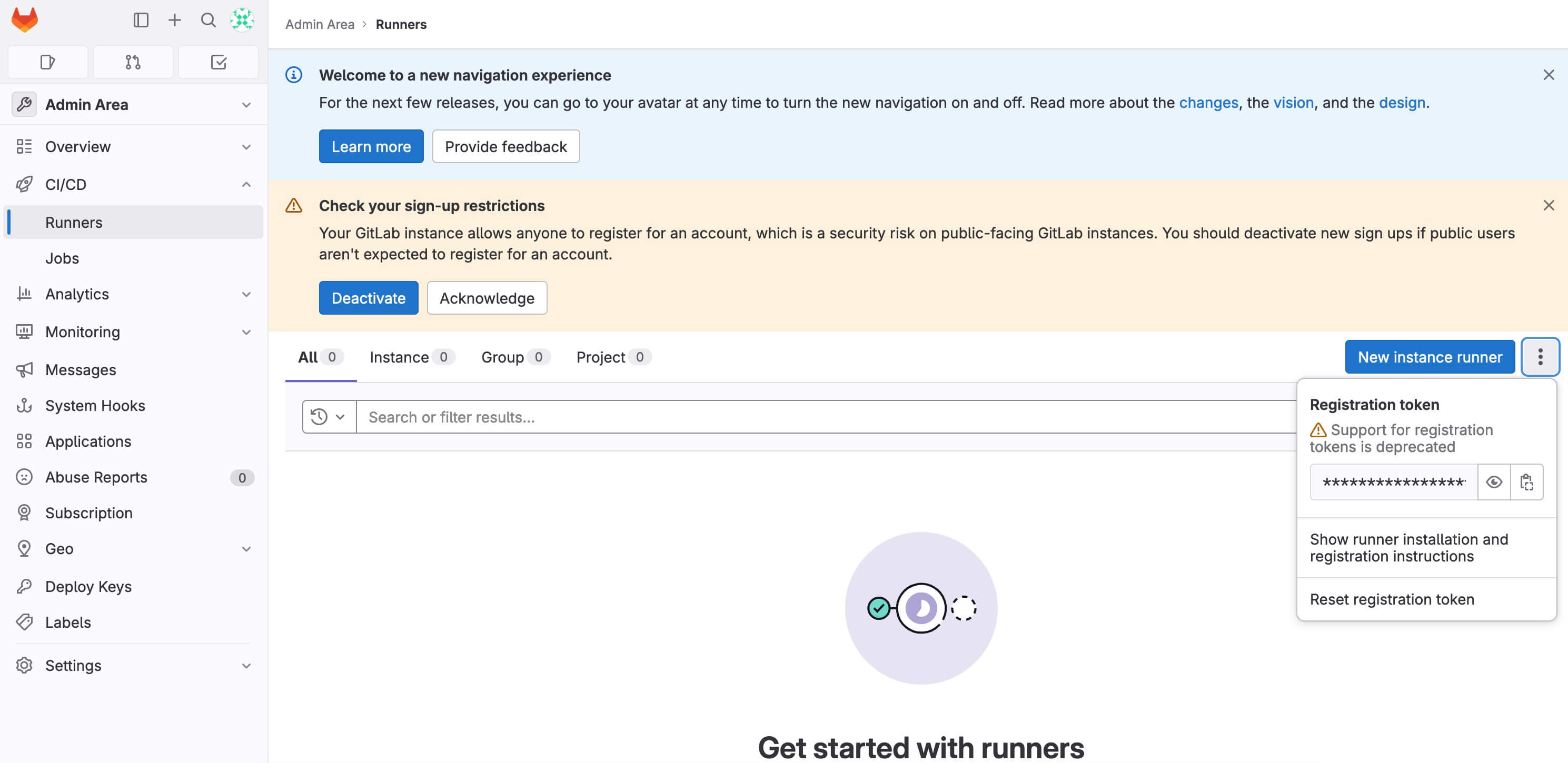
Next, let’s retrieve the registration token for the GitLab Runner and register it to handle upcoming CI/CD jobs.
GitLab Runner is the open-source project that is used to run your CI/CD jobs and send the results back to GitLab.
To view the GitLab Runner’s configuration, go to https://gitlab.heyvaldemar.net/admin/runners from your workstation, where gitlab.heyvaldemar.net is the domain name of my service. Accordingly, you need to specify your domain name that points to the IP address of your server with the installed Traefik service, which will redirect the request to GitLab.
💡 Note that you need to specify the domain name of the service, previously defined in the .env file.
Click on the three dots on the right to access the menu, then copy the registration token.
Next, let’s register the GitLab Runner.
Return to the Terminal emulator.
💡 Remember to replace REGISTRATION_TOKEN with the “Registration token” value you received in the previous step on the GitLab web interface.
To register the runner, use the following command:
REGISTRATION_TOKEN=LgcfPEKgawRTGR8P4uPQ \
&& docker exec -it $(sudo docker ps -aqf "name=gitlab-runner-1") gitlab-runner register \
--non-interactive \
--url "http://gitlab/" \
--registration-token "$REGISTRATION_TOKEN" \
--executor "docker" \
--docker-image docker:stable \
--description "docker-runner-1" \
--tag-list "docker,linux" \
--run-untagged="true" \
--docker-privileged \
--output-limit "50000000" \
--access-level="not_protected" \
--docker-volumes "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"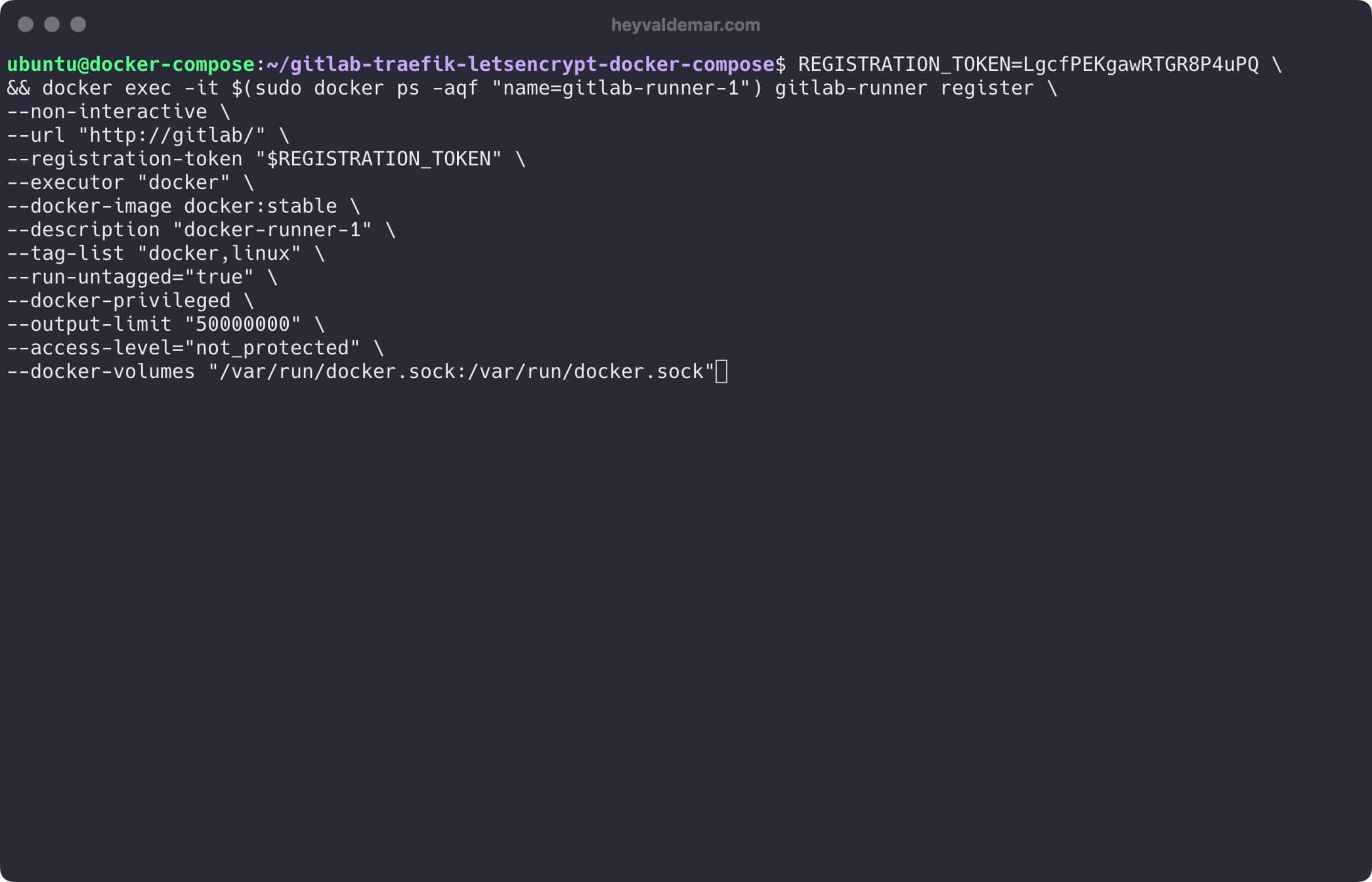
GitLab Runner has been successfully registered and is ready to work.
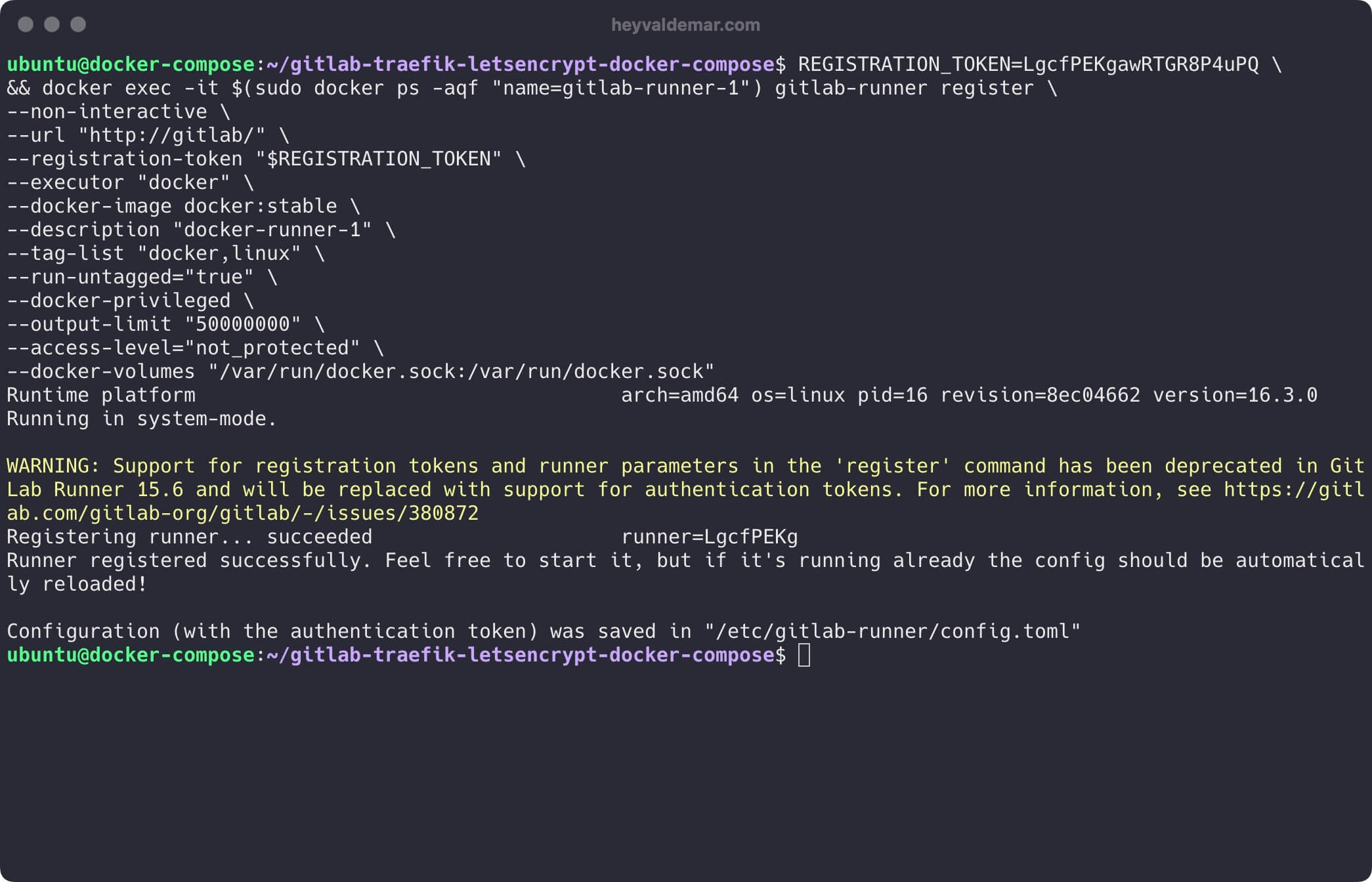
Return to the web interface and verify that the GitLab Runner is now online.
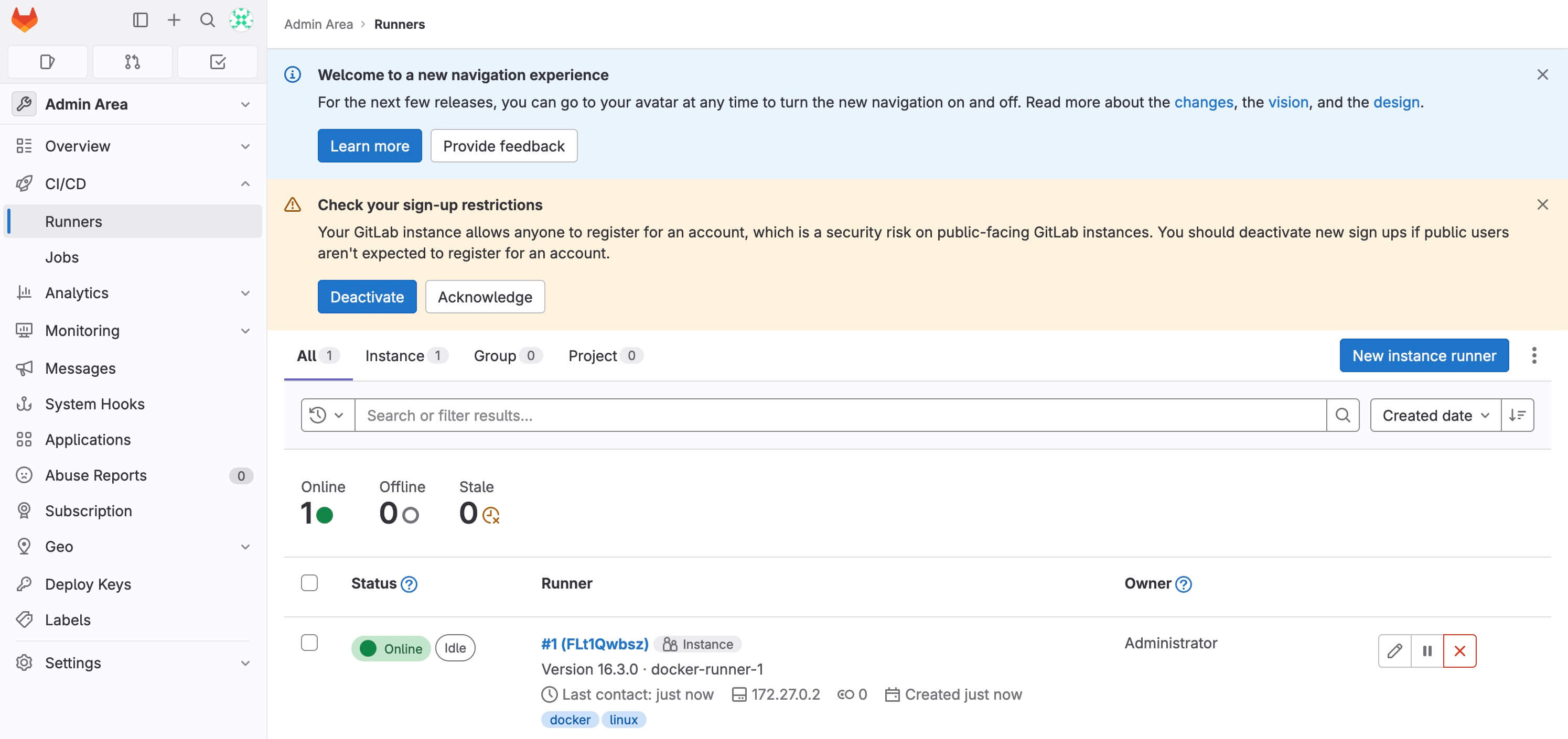
To access the Traefik control panel, go to https://traefik.gitlab.heyvaldemar.net from your workstation, where traefik.gitlab.heyvaldemar.net is the domain name of my service. Accordingly, you need to specify your domain name that points to the IP address of your server with the installed Traefik.
💡 Note that you need to specify the domain name of the service, previously defined in the .env file.
Enter the username and password previously set in the .env file, and click the “OK” button.
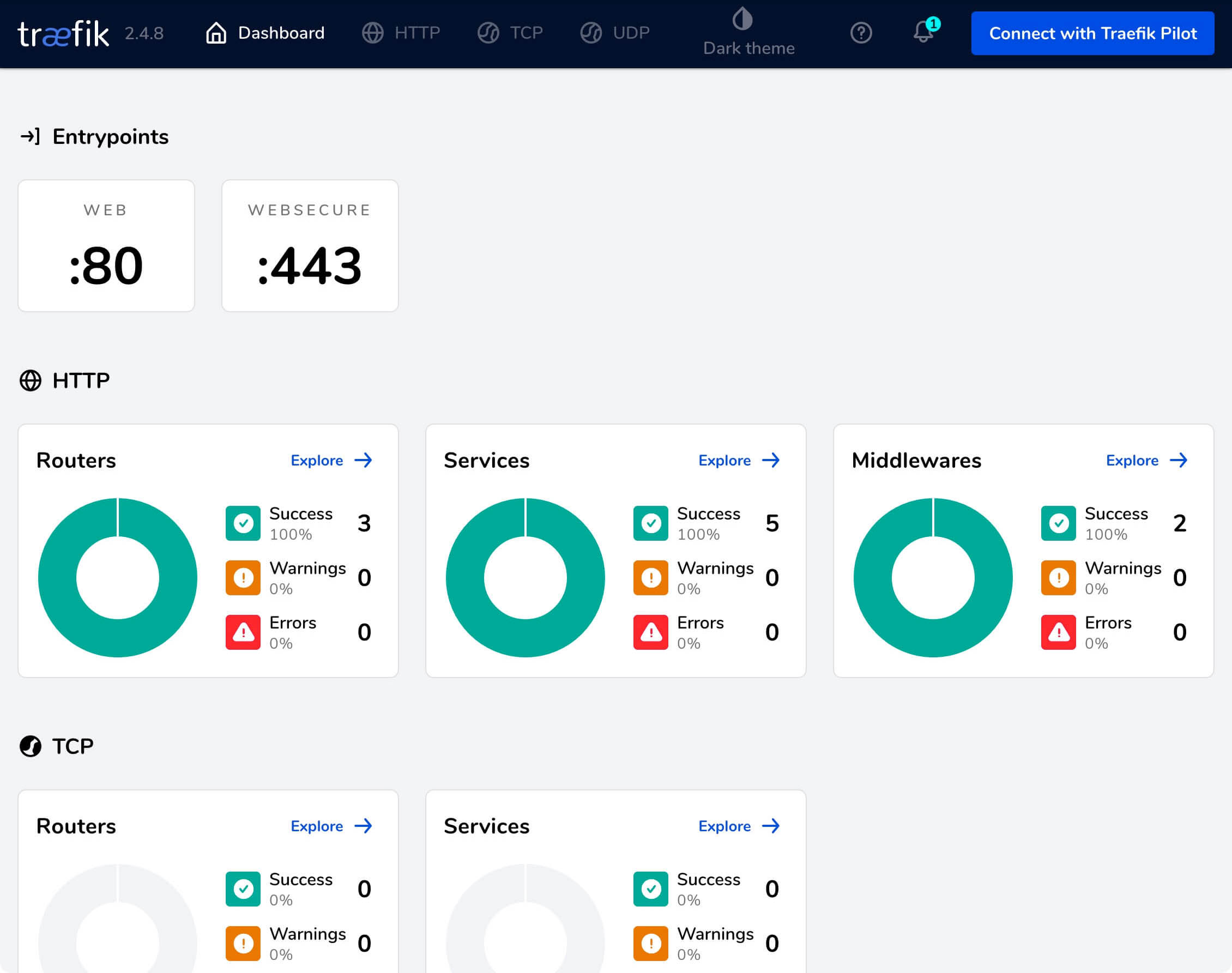
Welcome to the Traefik control panel.
Patreon Exclusives
Join my Patreon and dive deep into the world of Docker and DevOps with exclusive content tailored for IT enthusiasts and professionals. As your experienced guide, I offer a range of membership tiers designed to suit everyone from newbies to IT experts so you will get
What You’ll Get
🏆 Patron-Only Posts: Gain access to in-depth posts that provide a closer look at Docker and DevOps techniques, including step-by-step guides, advanced tips, and detailed analysis not available to the general public.
🏆 Early Access: Be the first to view new content and tutorials, giving you a head start on the latest technologies and methods in the IT world.
🏆 Priority Support: Have your specific questions and challenges addressed with priority, ensuring you get the most tailored and direct support possible.
🏆 Influence Future Content: Your suggestions and feedback directly influence the topics and tutorials I create, making sure the content is highly relevant and useful to your needs.
🏆 Recognition and Interaction: Active participants and supporters receive shout-outs in videos and public streams, acknowledging your important role in our community.
🏆 Special Discounts: Enjoy discounts on courses and future events, exclusively available to Patreon members.
🏆 Networking Opportunities: Connect with other IT professionals and enthusiasts in a supportive and engaging environment, expanding your network and learning collaboratively.
🏆 Heartfelt Gratitude and Updates: My personal thanks for your support, which fuels the creation of more content and allows continuous improvement and expansion.
Join me now and start your journey to mastering Docker and DevOps with exclusive insights and a supportive community!
My Courses
🎓 Dive into my comprehensive IT courses designed for enthusiasts and professionals alike. Whether you’re looking to master Docker, conquer Kubernetes, or advance your DevOps skills, my courses provide a structured pathway to enhancing your technical prowess.
My Services
💼 Take a look at my service catalog and find out how we can make your technological life better. Whether it’s increasing the efficiency of your IT infrastructure, advancing your career, or expanding your technological horizons — I’m here to help you achieve your goals. From DevOps transformations to building gaming computers — let’s make your technology unparalleled!
Refill My Coffee Supplies
💖 PayPal
🏆 Patreon
💎 GitHub
🥤 BuyMeaCoffee
🍪 Ko-fi
Follow Me
🎬 YouTube
🐦 Twitter
🎨 Instagram
🐘 Mastodon
🧵 Threads
🎸 Facebook
🧊 Bluesky
🎥 TikTok
💻 LinkedIn
📣 daily.dev Squad
🧩 LeetCode
🐈 GitHub
Is this content AI-generated?
Nope! Each article is crafted by me, fueled by a deep passion for Docker and decades of IT expertise. While I employ AI to refine the grammar—ensuring the technical details are conveyed clearly—the insights, strategies, and guidance are purely my own. This approach may occasionally activate AI detectors, but you can be certain that the underlying knowledge and experiences are authentically mine.
